Table of Content
Agile leadership is fundamentally about cultivating an environment where self-organizing agile teams can thrive. In the context of technology and digital transformations, this leadership style is critical, directly influencing an enterprise’s ability to build innovative products and thereby impacting its productivity, profitability, and market position.
Agile leaders achieve this by shaping organizational structures and fostering a culture of continuous improvement—skills often honed through practical experience in servant leadership and facilitation.
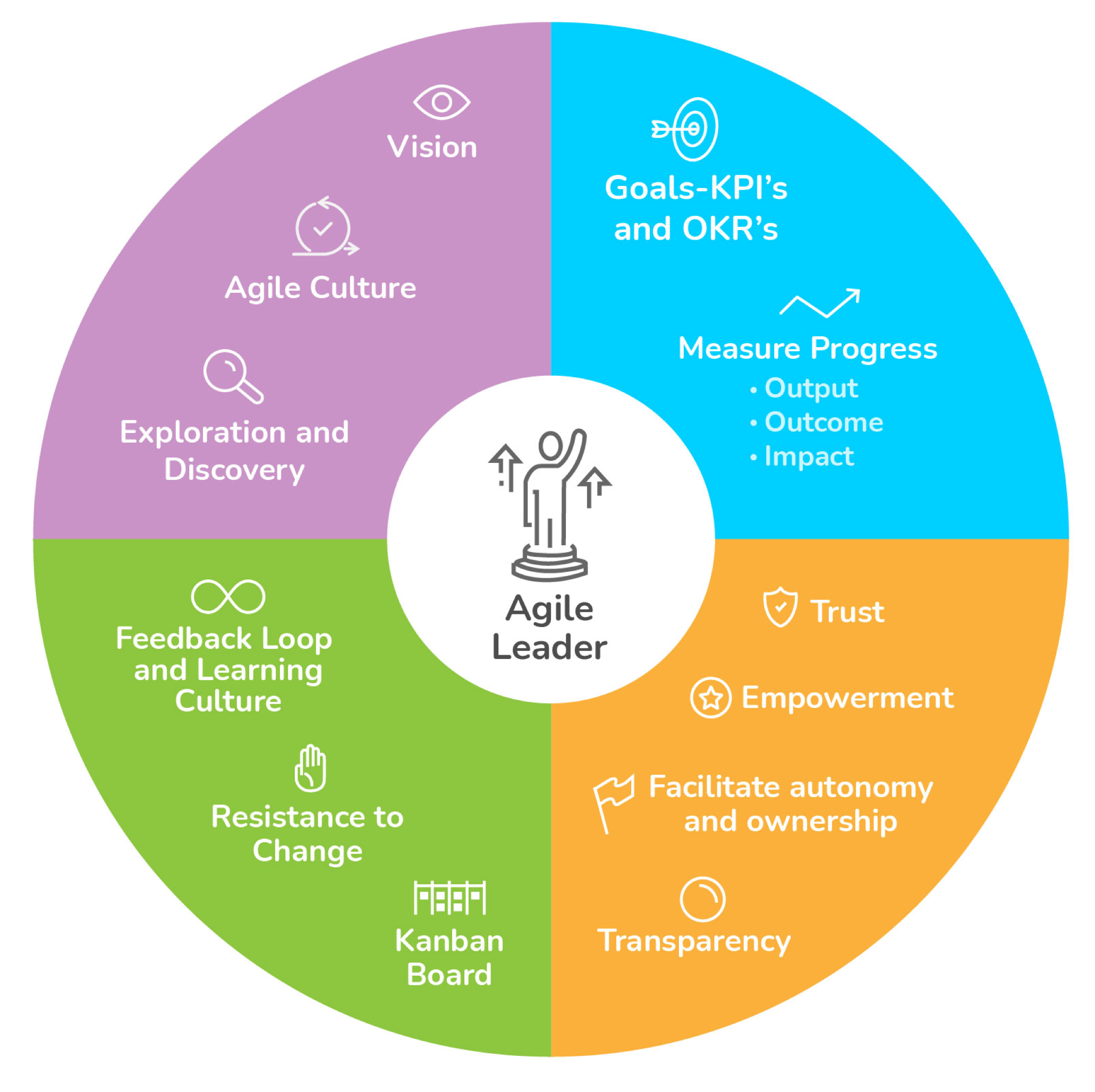
Agile Leadership Characteristics
Agile leaders are pivotal in fostering healthy teams and supportive organizational cultures. These elements, combined with strong technical practices and organizational capabilities, are significant predictors of software delivery performance. Such leadership actively cultivates the values, practices, and processes of agile development essential for developing robust team capabilities.
Team Goals
While Lean-Agile practices and technical proficiency are crucial for achieving goals, agile leaders specifically focus on setting customer-centric objectives. They define clear, measurable goals that deliver value to both end-users and the business, even in complex and uncertain environments, and guide the actions needed to achieve these deliverables.
Agile leaders empower teams to understand their purpose and refine processes by guiding them to measure how products impact user behavior and business value. They support teams in defining relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and leveraging product analytics/metrics to gain insights into achieving desired outcomes.
Team Vision
Agile leaders cultivate a strong sense of purpose by connecting team members to the product’s vision through the product roadmap and delivery process. They inspire creativity, encouraging input for innovative ideas and features. By embodying authenticity, these leaders articulate a clear vision for the team’s direction, support their journey of discovery, and provide honest, constructive feedback.
They foster customer empathy within the team, encouraging analysis from the user’s perspective and an understanding of customer assumptions. This helps teams co-create shared goals that benefit both the customer and the business. Agile leaders ignite passion for the product vision, helping teams understand how short-term outcomes contribute to long-term strategic objectives.
Collaboration and Communication
Agile leaders design team structures and communication patterns that promote a fast flow of information and facilitate seamless team interactions. Their communication is constructive and appreciative, fostering pride in the team’s accomplishments.
They organize teams around desired outcomes, fostering a collaborative environment within and between teams while respecting architectural boundaries and dependencies. Through active coaching, agile leaders nurture team members, facilitate collaboration, and encourage growth.
Team Autonomy and Ownership
A key characteristic of agile leadership is empowering teams to take full ownership and accountability for their projects. Leaders encourage proactive problem-solving and solution-finding, fostering a sense of ownership that is strengthened by overcoming challenges and learning from experimentation.
Agile leaders actively encourage and inspire team ownership. While they might intervene to balance or support based on situational needs and team maturity, their primary role is to enable ownership by cultivating the right mindset, asking guiding questions, providing training, and ensuring processes and environments conducive to high performance.
They grant autonomy thoughtfully, aligning the level of freedom with the team’s maturity and context, while always providing guidance and support for decision-making. Leaders leverage Agile frameworks (e.g., Scrum, SAFe, LeSS) to assess team alignment and cultivate an environment where ownership and accountability can flourish, ultimately helping teams reach their highest potential.
Continuous Feedback
Agile leaders champion an environment of open feedback and a continuous learning mindset. This extends beyond internal processes to actively promoting and integrating feedback from product users throughout all development stages, enabling timely adjustments.
They utilize the feedback loop as a critical learning cycle to assess team organization and effectiveness. Agile leaders strive to optimize this loop by reducing lead times and measuring flow (e.g., velocity, throughput, work in progress) to ensure efficient value delivery. Techniques like Kanban or visual management boards are employed by agile leaders to enhance transparency and track progress, particularly during iterative cycles. The learning process is synchronized with delivery frequency, ensuring insights from each iteration inform the next.
Furthermore, agile leaders dedicate time and resources for individual and team learning, supporting exploration of new technologies and methodologies. They foster organizational learning by creating platforms for knowledge sharing through various activities and events.
Agile Culture
Agile leaders are architects and stewards of an Agile culture. They model the desired thinking, mindsets, and behaviors, thereby motivating and inspiring teams to embrace change. Cultivating or transforming organizational culture involves influencing teams to adopt Agile-aligned behaviors and attitudes, establishing healthy habits over time. Leaders continuously analyze cultural elements, review capabilities, and explore adjustments to enhance business agility.
Cognitive Stimulation, Supportive Leadership, and Recognition
Agile leaders intellectually stimulate their teams, challenging them to critically assess products, organizational structures, and processes, and encouraging creative problem-solving. They consistently recognize achievements and provide support, considering individual interests and offering intrinsic motivators over extrinsic rewards.
Through consistent coaching, leaders support team members in developing both their technical practices and self-organization capabilities. This helps individuals adopt beneficial behaviors and contribute their best within a psychologically safe environment conducive to innovation.
Agile Leadership: Spearheading DevOps Transformation
Recognizing DevOps practices as a crucial predictor of superior software delivery performance, agile leadership plays a pivotal role in not just promoting but strategically orchestrating their adoption. This goes beyond general team enablement to encompass:
- Architecting the DevOps Transformation Strategy: Leaders organize and set strategies to adopt DevOps capabilities. This involves creating a clear vision and a transformation plan with clearly defined outcomes. Agile leaders champion this roadmap, ensuring it addresses how to scale the DevOps culture effectively and sustainably across the organization. They define what success looks like and how progress will be measured.
- Championing a Unified Value Stream and Culture: Agile leaders actively work to break down historical silos between development, operations, QA, and security (DevSecOps). They foster a shared understanding and ownership of the entire value stream, from ideation to product launch. This involves promoting cross-functional collaboration, aligning incentives, and addressing the cultural shifts required to move from disparate functions to integrated DevOps teams.
- Driving Strategic Tooling and Automation Investment: Agile leaders don’t just implement tools—they drive toolchain integration. They advocate for and secure investment in foundational automation and tooling (e.g., CI/CD pipelines, comprehensive automated testing, Infrastructure-as-Code) that are critical for DevOps success. They ensure these tools are chosen and integrated not as isolated solutions, but as enablers of the overall DevOps strategy and value stream efficiency.
- Enabling Technical and Architectural Evolution: Successful DevOps often requires an evolution of technical practices and system architecture (e.g., adopting microservices, building test automation and deployment resilience, ensuring observability). Agile leaders support and empower teams to make these necessary changes, understanding that the right technical foundations are essential for realizing the speed, stability, and reliability benefits of DevOps.
- Removing Systemic Organizational Impediments: Agile leaders look beyond team-level blockers to identify and remove broader organizational impediments. These might include outdated governance models, misaligned performance metrics, or risk-averse policies that hinder experimentation and the adoption of new DevOps ways of working.
By focusing on these strategic areas, agile leaders create the organizational conditions, secure the necessary resources, and drive the cultural and technical changes essential for DevOps practices to deliver their full impact on performance and business agility.
Key Takeaway
Agile leadership builds the right environment for self-organizing teams to operate with autonomy and ownership. Teams implement a feedback loop as a learning process and improve their processes and products continuously. Each organization and team has its own environment and context, cultures, mindsets, and individuals that must be modeled to reach operational performance.
Developing a Generative culture (as defined in Westrum’s typology) is the product of experimentation and learning specific to the situation and the company culture.
Agile leaders lead by example to build high-performing teams and thrive in fast-changing environments, understanding tools, rules and elements, while exploring different approaches to overcome challenges and become an agile organization.
Krasamo is an agile development company with more than 15 years of experience building Agile teams and leading software development projects in IoT, mobile development, web development, artificial intelligence, and digital transformations.








I totally get where you’re coming from – it can be tough to prioritize feedback from product users, especially when there’s a lot on the plate! Have you considered incorporating scrum master training into your team to help facilitate this process? 🤔💡
I’m living proof of this! In my previous role as a software architect, I recall when our scrum master training helped us shift focus from traditional “code-complete” milestones to business value-driven goals. It was a game-changer for our team’s productivity and user satisfaction!
I’d love to hear more about cultivating an agile culture through effective agile leadership practices
I found this post to be quite thought-provoking regarding Agile Leadership principles. I would like to add that lean software development methodologies can also play a vital role in fostering an environment where self-organizing teams can thrive. By embracing lean principles such as continuous delivery, value stream mapping and eliminating waste, organizations can create a more efficient and agile culture that supports rapid innovation and improvement. This approach can complement Agile Leadership and contribute to the success of development teams.
I appreciate the emphasis on building a generative culture through experimentation and learning. However, as someone familiar with the Agile methodology, I would have liked to see more concrete examples of how this is implemented in practice.
I must say, I’m not entirely convinced by the notion that Agile leadership is solely about creating an environment for self-organizing teams to thrive. Don’t get me wrong, agile management is crucial, but surely there’s more to it than that? 🤔