Table of Content
- Discovery State for Creating an App
- Planning for How to Create an App
- Analizing the Problem or Oportunity
- UI/UX Phase
- Exploratory Research Methods for Creating an App
- UX Design Techniques for Creating an App
- How to Create an App—Development Stages
- Programming (Code the Solution)
- Quality Assurance (Code Testing)
- Continuous Delivery (Deployment)
- Adopt Continuous Delivery and DevOps Practices
- Create a Deployment Pipeline
- Continuous Deployment
- Version Control of Systems and Processes
- Release into Production Phase
- Getting Feedback and Measuring Success
- Submit the App to the App Store
- Key Takeaway
Discovery Stage for Creating an App
Once the app idea is born, marketing and UX researchers collect data and address the opportunities and offerings that align with the business goals and objectives. At this early stage, managers look into product potential, market size, competition, and the needs and attitudes of end users.
During the discovery stage, a process of generating ideas (ideation stage) without judgement takes place to understand the real user needs prior to the definition of the problem, its solution, and development of the concept.
As a first step in creating an app, agile leaders align and integrate their marketing team with UX design teams to ensure effective communication and collaboration.
Planning for How to Create an App
A project manager (or scrum master), together with his or her team, is responsible for delivering a final product. An agile team structure with the necessary skillset, resources, and knowledge base is vital to how the app is created and its future success.
The agile team defines a clear mission and concrete goals and then aligns the project team members to avoid friction during the app development process.
Analyzing the Problem or Opportunity
Developers must also define use cases and functional requirements in order to prepare the product roadmap for creating deliverables and building a minimum viable product (MVP).
UI/UX Phase
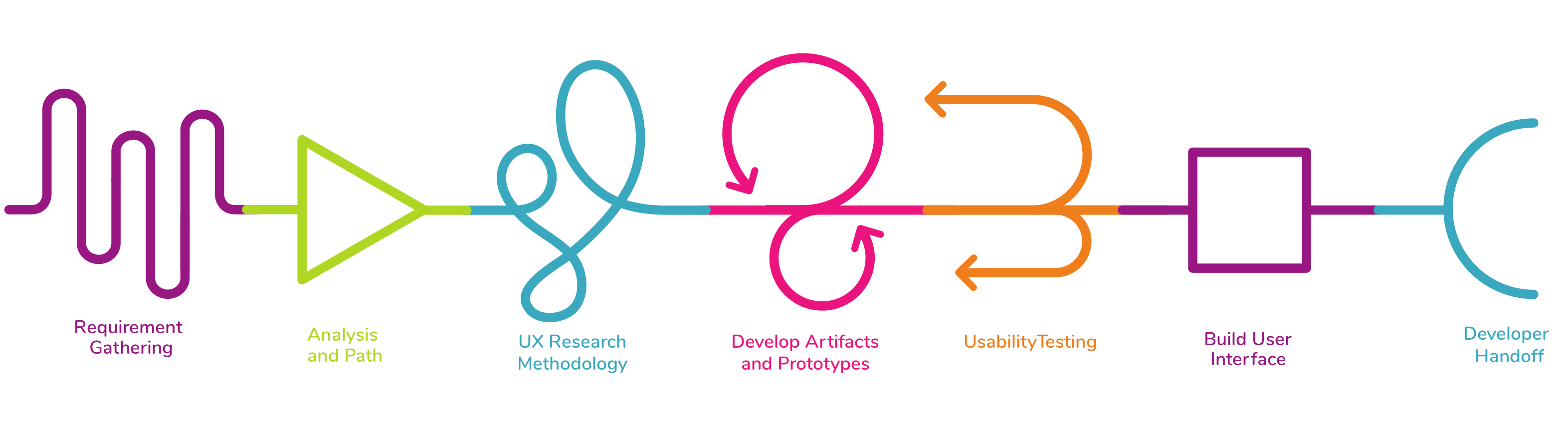
- Requirement gathering
- Analysis and path
- UX research methodology
- Develop UX/UI artifacts and prototypes
- Perform usability testing
- Build user interface
- Handoff to developers
UX researchers and UX designers learn and understand users by combining research approaches to ensure that app features will address user needs. Challenging assumptions and avoiding bias, they are continuously exposed to research data and observations to contribute to the design process during the app creation lifecycle.
Interviewing users and observing behavior helps to gather actionable and testable data about user needs within the context of the real situation (contextual inquiry). User stories are created from UX research methods and frameworks of observation.
UX and UI designers apply lean-agile methods that continuously refine the product in response to user feedback, while also gathering insights, developing artifacts and prototypes, and validating the solution through usability testing.
App functionality is continuously adapted to user needs by leveraging qualitative and quantitative systems to measure user activities and aligning tasks with objectives following the product roadmap and prioritizing usability.
Following an iterative process, an app is designed after UX and UI professionals align the design and user information with company objectives and the solution the app will provide.
Exploratory Research Methods
for Creating an App

Focus Groups

User Personas

Competitor Studies

Remote User Research

Diary Studies

Field Studies

Surveys

User Journey Mapping

User Interviews

Expert Reviews

Card Sorting
Affinity Diagramming
UX Design Techniques for Creating an App
Design teams create the information architecture with specific data about the interface and functionality, user journeys, and workflows of user interactions and navigation structure. Also, they create a style guide with the design standards and branding information to ensure consistency in the look and feel of the app.
Designers are in charge of creating the design interface between users and the app in order to ensure its usability by adopting a hands-on approach of experimentation with techniques, constantly challenging assumptions. The interface involves the layout of visual elements (icons, buttons, themes, colors, backgrounds, etc.) and the interactions with the user.
UI/UX designers create proof-of-concept (PoC) such as wireframes and prototypes that ensure effective testing and validation focusing on the problem to be solved. Also, as a best practice, they continuously conduct and monitor user interface (UI) testing, A/B testing, usability testing, and other UX techniques.
Sketching
Storyboards
Interactive Screens. A series of screens (without navigation) are created for testing purposes.

Wireframes

Low-Fidelity Prototypes

Low-Fidelity Mockups

A/B Testing

Interactive Prototypes
Usability Testing
How to Create an App—Development Stages
Mobile app development is the process of coding software that runs on mobile devices (front-end) and is connected to other computing resources. It involves creating software bundles, back-end services, and APIs, and it involves continuous testing. Developers create the logic and build code for the communication of components.
Once you define the mobile platforms (iOS or Android) discuss with your team the software stack, toolchain, software development kits (SDKs), and the necessary skillset to ensure you can deliver on time and within your budget. Also, make sure you have a clear definition and the implications of developing native and/or cross-platform applications.
Choose the appropriate technology stack, programming languages, frameworks, setup development environment, and tools and techniques, and ensure that your team understands how to create an app with a supportive data system with APIs.
Agile teams use product roadmaps, releasing plans that are aligned with their capacities and velocities and reviewing them during sprint planning events.
Programming (Code the Solution)
Front-End. The front-end is the code that resides on the device and creates the interactive and visual aspects of the app. The front-end relies on data from back-end services that are connected by APIs. Creating an app requires skilled developers in front-end frameworks and languages that create the logic to call on back-end services, pull data, and update back-end services from data generated by the user.
Back-End. The back-end is the code that supports the mobile device (front-end). Developers create services that suit their applications and add existing cloud-based services to increase their capabilities and maintain their infrastructure.
APIs. Application programming interfaces (commonly called APIs) are the code that facilitates the communication between the front-end, back-end, and other applications. Make sure you hire programmers who have skills in creating and connecting APIs and integrating services through software development kits (SDKs).
Quality Assurance (Code Testing)
Testing is a process that simulates usage behavior and requires creating scripts according to product requirements. Testing a mobile app is a key aspect of creating an app, and testing has its own challenges due to the variety of device models and versions as well as operating system versions with different properties that require writing many scripts.
QA engineers create scenarios and convert them to test cases to determine if features are working correctly. They also analyze app components and perform manual or automated tests to optimize usability, functionality, and performance throughout the app development lifecycle.
App developers focus on preventing defects and correcting errors before delivering app features; they also check requirements and test the stability of systems and layers before working on stories, components, and subsystems.
QA testers must understand how users interact with the product, features, and stories so they are able to write executable tests that guide developers in writing good code.
QA testers work by implementing test management tools, which are integrated with the development environment, testing virtual devices from emulators within the integrated development environments (IDE). Using physical devices, together with third-party tools, they are able to detect bugs with greater precision. Testing is performed manually and gradually automated.
The QA team should be synchronized with other teams and must be familiar with DevOps practices to maintain the flow of the delivery pipeline.
QA testing can be functional, nonfunctional, or for maintaining the app after its release. Continued testing helps to identify context; define use cases, testing types, tools, and scenarios; and sets up testing environments and software testing activities for creating your app successfully.
Building a successful QA team is a critical step in how to build an app, as they can recommend tools for testing, alerting, monitoring, logging, test suites, defect tracking, etc.
Continuous Delivery (Deployment)
Developers’ productivity depends on reliable and stable systems that will enable them to code and implement features productively. For this to happen, you need an IT team managing operations and infrastructure effectively to respond quickly to avoid accumulation of problems. Developers need to have the tools, platforms, and capabilities to work productively.
The integration of IT, QA, and security team into the development team is critical to the success of the app being created, as this will reduce handoffs and provide a safe environment without conflicting teams. Development and operations (DevOps) combine their efforts to increase velocity, reliability, and shared ownership to reduce the development cycle and optimize continuous delivery (CD).
Adopt Continuous Delivery and DevOps Practices
Software development is supported by adopting continuous delivery (CD) and DevOps practices. Continuous delivery is a way of working that includes all the practices from idea to delivery of software processing in parallel. Therefore, it requires technical knowledge, organizational structure, and performance.
DevOps practices promote self-sufficient and cross-functional teams with visibility and control in order to deliver features and run code without dependencies.
Continuous delivery is the technique practiced by empowered teams working in small steps (batches), sharing responsibility, committing changes, and testing iteratively to maintain the code in a releasable state—a key aspect of how to build an app.
Create a Deployment Pipeline
In their work, developers focus on using an agile development process, which involves constantly experimenting while also reducing waste and improving lead time and stability.
Organizing the activities of continuous delivery and automating them effectively leads to the implementation of a deployment pipeline. The development environment is set up with all the tools, network access, operating systems, hardware, languages, VCS, etc.
Agile teams create a deployment pipeline that encompasses all the activities of the development process until code is released into production. All code is deployed as an independent unit and is tested for failure while running other tests in parallel.
A deployment pipeline is a process structured in stages. The commit stage is where code is compiled and unit tests are run to support programming. Other stages include creating a build management system (BMS) (Jenkins), setting up a version control system (GitHub), and creating repositories, acceptance stage tests, configurations, automations, and other activities.
Continuous Deployment
Once the pipeline and production environment are established and optimized, developers choose the approach to release to production (manual releases or automated deployments). Continuous deployment is achieved when all changes are deployed to production automatically.
There are other essential practices that help to optimize the deployment pipeline, such as test-driven development, version control, and automation of repeatable process of build, infrastructure, data migration, monitoring, and reporting.
Version Control of Systems and Processes
Version control is the system for managing changes and ensuring they are reproduced consistently. VC aims to have a current version of the system and continuous integration between developers with reduced branching. VCS is used to manage configurations of infrastructure variables that are needed to reproduce the system.
Release into Production Phase
After the code has been tested and deployed as a release candidate many times and developers are certain that it works, they push the code into production. In continuous deployment, the code is automatically deployed into production.
Getting Feedback and Measuring Success
The next step in how to build an app is monitoring feedback of technical and functional information and gathering information for business decisions. The success of the app must be measured to ensure it serves its purpose and to evaluate its stability and efficiency (throughput).
Getting feedback from users will help ensure that the app meets the requirements and solves the problem. The agile team meets during the sprint review and retrospective to discuss the improvements for the next sprints.
The team also measures performance and learns about the app’s velocity in context to understand the team’s execution predictability.
Submit the App to the App Store
The next step is to prepare the app for submission following the app store guidelines and process for approval. This will include setting up your integration development environment (IDE) software to connect and upload the app to the store (XCode for iOS Apps and/or Android Studio for Android App Development).
Key Takeaway
One of the main aspects to think about with regard to how an app is created is to consider the application of lean-agile UX design principles and techniques. Discuss with your team the software stack, toolchain, software development kits (SDKs), and the necessary skillset to ensure that you can deliver on time and within your budget.
Using an agile development process, DevOps practices, and continuous delivery for creating your app will ensure better outcomes, including increased speed and reliability. Continuous delivery is an incremental and iterative approach to develop software to build apps, and it is the primary tool for gaining operational performance and avoiding digital disruption.
A deployment pipeline encompasses all the activities of the development process until code is released into production. Enterprises employing these techniques are more likely to retain developers and develop products faster. This higher pace of innovation will lead to significant competitive advantages.