Table Of Content
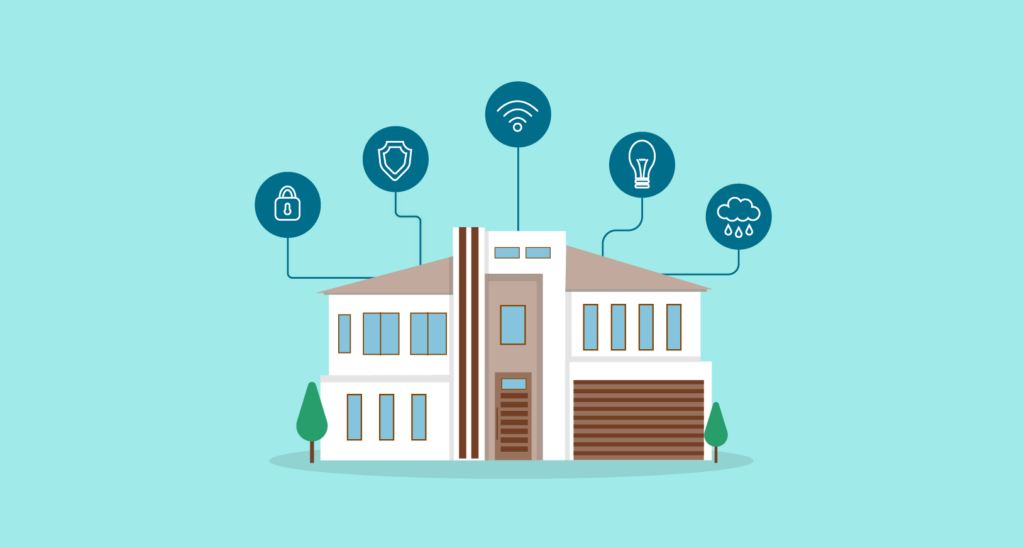
Monitor and manage data about the presence of people in a space and flow in buildings—control building systems based on occupancy.
This paper is part of the content series for IoT applications for smart buildings. We discuss occupancy sensing and the main benefits of detecting presence and occupancy for improving smart building solutions.
- Increase Occupant Comfort—Improve user experience and efficient space utilization.
- Energy Efficiency—Optimize HVAC, lighting, heating, and ventilation systems in buildings based on the number of occupants.
- Security and Access Control—Track and monitor movement of people, restricted areas, and unauthorized access.
- Enhance the Safety of Smart Buildings—Trigger emergency responses using data about occupants and location within the building.
- Monitor and Manage People Flow/Density—Capture real-time occupancy data using image/video or sensor-based monitoring systems.
- Improve Building Maintenance—Prioritize maintenance areas and schedule efficiency of operations.
What Are Occupancy Sensors?
Occupancy sensors, also called motion sensors, are the sensing elements that detect the presence of people. They are used to calculate the duration of occupancy or count the number of occupants and use that information to automate the building systems. The most common types of occupancy sensors are the following:
Passive Infrared (PIR)—sense or detect changes in infrared radiation emitted by human body heat using a pyroelectric element.
- Ultrasonic—measure the bounce return time of waves emitted by moving objects.
- Microwave—analyze low-powered microwave signals that bounce from objects/people.
- Dual Technology—detect occupancy when PIR and ultrasonic or PIR and microwave signals are detected.
- Vision Sensors—use cameras and computer vision algorithms to analyze individuals and crowd behaviors.
- Acoustic Sensors—analyze sound patterns.
Occupancy Sensors vs. Motion Sensors
Understanding the difference between occupancy and motion sensors is important, as these terms are often used interchangeably.
- Occupancy Sensors. Occupancy sensors detect the presence of humans and determine the occupancy/vacancy of spaces commonly used in smart buildings for HVAC, lighting, and space optimization. They use the same technologies in combination with computer vision.
- Motion Sensors. Motion sensors detect physical movement in a specific area of any object, person, or animal. They are used in security and outdoor lighting systems to control movement within a space. Motion sensors detect movement using passive infrared (PIR), ultrasonic, or microwave technologies.
How Do Occupancy Sensors Work?
Occupancy sensing is a technology for detecting the presence and movement of people in buildings or spaces that integrates with smart building solutions to optimize resources and enhance sustainability.
Occupancy sensing generates real-time data from sensors (IoT sensors) that IoT systems interpret and use to create functionality and automate buildings.
The raw sensor data is conditioned (filtering, amplifying, and removing noise) to remove noise and ensure an accurate representation of occupancy levels. This process is done within the sensor. The signal conditioning circuitry is integrated into the sensor module or the circuit board (PCB).
Then, the analog signal is converted to digital signals and transmitted to the microcontroller with an integrated (ADC) or digital signal processor (DSP) for further processing.
Data from multiple sensors is aggregated, preprocessed, and validated. Then, data is converted to a standard format for further analysis and storage.
The microcontroller processes the occupancy sensing information or analyzes the signals to understand the occupancy status, applies logic to improve accuracy, and sends commands to control the building systems.
Occupancy sensing systems generate insights from usage patterns, trends, and behaviors about energy consumption and comfort levels—following predefined rules and algorithms that trigger actions to make informed decisions for controlling building functions (lighting, air conditioning, heating, and ventilation).
The microcontrollers run the firmware that governs and manages IoT sensors and their interactions with other devices, IoT gateways, and cloud platforms. They communicate through protocols (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or LoRaWAN) and manage data processing, control functions, sensor power-saving strategies, and decision-making.
Data is stored and integrated into other systems and machine learning models to improve the accuracy of occupancy detection and optimize performance and energy consumption.
IoT consulting engineers add occupancy sensors as part of the IoT system for smart buildings and create customized machine learning use cases that work with real-time data collected from IoT sensors.
Takeaway
Occupancy sensors play a vital role in enhancing smart buildings’ efficiency, comfort, and security. By monitoring and managing the presence of people and controlling building systems based on occupancy, these sensors contribute to improved user experience, energy efficiency, security, and safety. Employing various technologies, such as PIR, ultrasonic, microwave, and vision sensors, occupancy sensing enables smart buildings to optimize resources and adapt to occupants’ needs, ultimately creating more sustainable and intelligent environments.
Krasamo Works With Key Technologies
C/C++

Linux
Board Support Package (BSP)

Rust (Language)
FreeRTOS
Bluetooth/BLE
BLE Mesh
Embedded Wi-Fi

Flutter Apps

Dart
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)










Im low-key impressed with this blog post 🤓 It’s actually decent, but let’s be real, occupancy sensors and smart building are concepts I’ve been tooting about on my TikTok for years. The explanation of how they work is solid, though – you even got the IoT tech part right. Congrats on getting it somewhat correct 😎
I gotta disagree with the blog post – saying “occupancy sensors use computer vision” is a bit misleading, as most occupancy sensors rely on PIR or ultrasonic tech. Smart building vibes, but some facts are lacking
I thoroughly enjoyed your engaging blog post on Occupancy Sensors: Elevating Smart Building Performance! I agree that detecting presence and occupancy is crucial for enhancing smart building solutions. One minor suggestion I have is to elaborate on the integration of various sensors, such as those used in conjunction with occupancy sensors, like pressure pads or infrared cameras. Additionally, discussing the potential for AI-powered analytics would further bolster the benefits of occupancy sensing in achieving optimal smart building performance.
I completely concur with the author’s assertion that occupancy sensors play a vital role in enhancing smart building performance. Building on this concept, it would be intriguing to explore the integration of various sensors, such as pressure pads or infrared cameras, and discuss the potential for AI-powered analytics to further optimize smart building solutions. This added layer of sophistication could significantly bolster the benefits of occupancy sensing in achieving optimal smart building performance.