Wi-Fi enhances IoT device interoperability for high performance and business transformation.
Wi-Fi is a wireless connectivity protocol based on the 802.11 wireless communication standard and several generations of technologies, Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, and Wi-Fi 7 (expected to be released in 2024). In addition, Wi-Fi technology has backward compatibility, allowing older devices to interoperate with new devices in the network.
Wi-Fi names describe the technology contained in the IoT device as well as the type of network connection, identified by a numerical sequence that matches the version advancements in 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz radio frequency (RF) bands.
- Wi-Fi 7 uses 802.11be technology
- Wi-Fi 6 uses 802.11ax technology (6GHz)
- Wi-Fi 5 uses 802.11ac technology (5GHz)
- Wi-Fi 4 uses 802.11n technology (2.4GHz)

The Wi-Fi Alliance is an organization with a certification program for products (the Wi-Fi CERTIFIED™ seal of approval) that ensure interoperability, compatibility, and security protections. The 6GHz spectrum is unlicensed (license-exempt) and has 160 channels of uncongested bandwidth delivering multigigabit Wi-Fi.
IoT Wireless Connectivity
The growing consumer requirements and demanding use cases require a highly reliable network with the capacity (low latency) to consistently connect many devices (densification) at high speeds simultaneously (High Band Simultaneous Multi-Link).
IoT applications using Wi-Fi provide robust connectivity, fast uploads, strong WPA3 security protocols, and robust authentication to protect information and support environments. Wi-Fi also provides exact location information for IoT services, such as asset tracking, location services, logistics, geofencing, etc.
IoT devices can extend the Wi-Fi range (approximately 1km) and low power connectivity using Wi-Fi HaLow, which operates in the sub-1GHz band. It is also used for challenging environments with barriers that require a strong connection. In addition, Wi-Fi HaLow is for devices that can operate with batteries for months or years.
Wi-Fi complements the deployment of other technologies, such as cellular communications and Bluetooth, where connectivity issues might arise. Many SoCs (system on chip) support features of dual bands (Wi-Fi + Bluetooth).
Benefits of Wi-Fi for IoT

Cost-effective

Low latency suited for enterprise and industrial IoT

Low latency suited for enterprise and industrial IoT

Faster uploads for multiple users (multiple-input multiple-output: MIMO)

Low power and sleep modes improve IoT device battery life and efficiency (target wake time: TWT)

Extended coverage range in dense and congested environments

Extended coverage range in dense and congested environments
Applies to transmit beamforming techniques to increase signal transmission and network capacity at specific ranges
Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6 Capabilities
- Orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA). Shares channels for lower latency in uplink and downlink traffic.
- Target wake time (TWT) improves IoT devices’ battery life
- Multi-user multiple input, multiple outputs (MU-MIMO). Enables access points to handle more IoT devices and transfer higher data loads.
Wi-Fi for IoT Use Cases
Applications that require high bandwidth and low power:

Smart home automation

AR/VR—metaverse and 8k streaming

Smart cities

Healthcare

Industrial IoT (IIoT)

Agriculture
Home security surveillance

Connected cars
Benefits of Partnering for Implementing Wi-Fi in IoT Projects
• Review of hardware designs (PCB) and Gerber files by subject-matter experts
• Wi-Fi next-generation product design and customized functionality
• Design products from existing qualified solutions
• Assistance in development of innovative products designed to meet Wi-Fi CERTIFIED™ product requirements
• Testing of Wi-Fi components and functionality
• Select optimal Wi-Fi device
• Develop embedded software
Wi-Fi Connectivity Solutions
Wi-Fi Modules
Wi-Fi modules are electronic components with integrated and defined radio frequency (RF) protocol standards to build IoT products with embedded Wi-Fi.
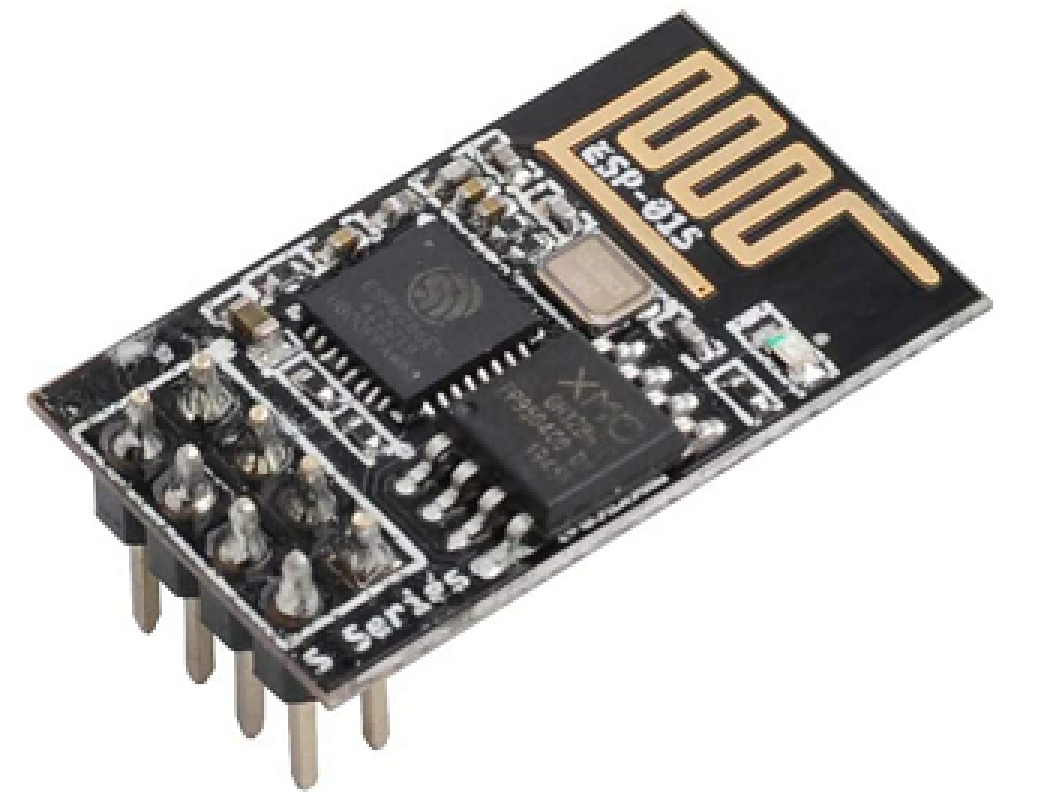
ESP8266 Wi-Fi Module. Connect your microcontroller or Arduino board to the internet by adding an ESP8266 Wi-Fi module. (ESP8266 Wi-Fi module Arduino)
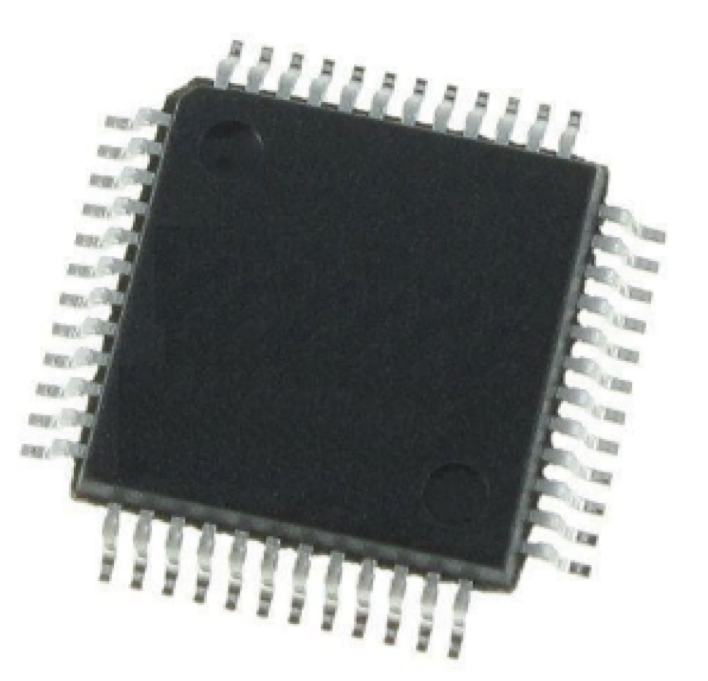
Wi-Fi System on Chip (SoC)
A system on chip (SoC) is a low-power chip (integrated circuit) that integrates components into a single chip, maximizing functionality and allowing faster development of an entire application with reduced software requirements.
Wi-Fi Wireless Microcontrollers (MCUs)
Microcontrollers are integrated circuits, similar to systems on chip (SoC), with CPU, memory, and peripherals, designed for embedded applications.
PIC32MZ-W1 Wi-Fi SoC. The PIC32MZ-W1 is a low-cost, high-performance 32-bit microcontroller (MCU) with industrial Wi-Fi connectivity.

IoT Development Boards
IoT development boards are integrated Wi-Fi MCU modules that support Wi-Fi functionalities and features. Using a development board is an effective way to connect embedded apps to IoT platforms. Boards may have sensors to collect and transmit data and can be connected to other peripherals.
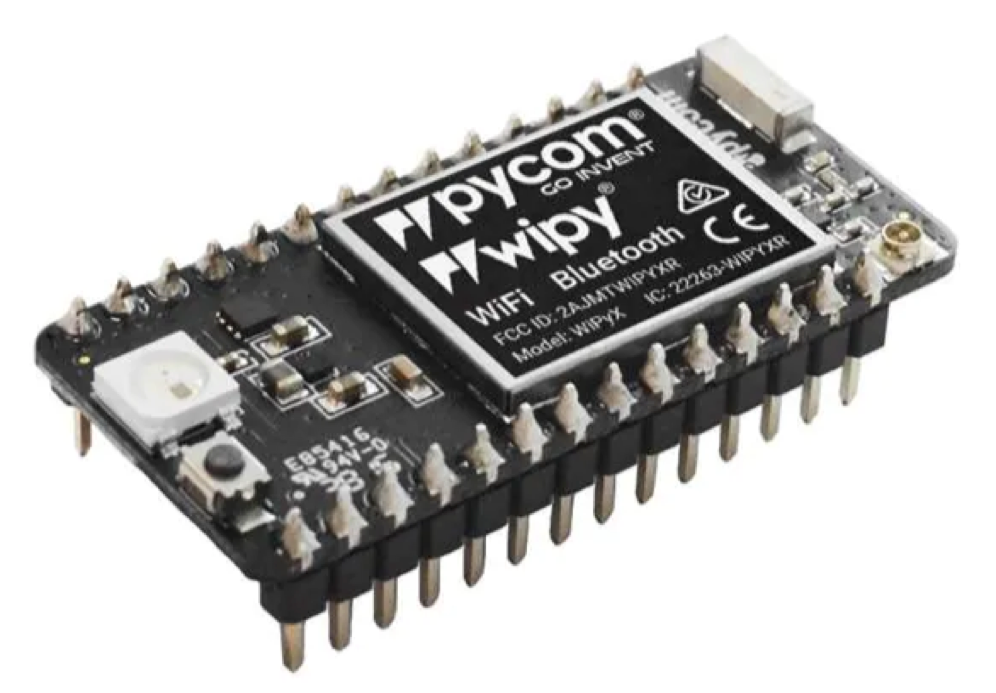
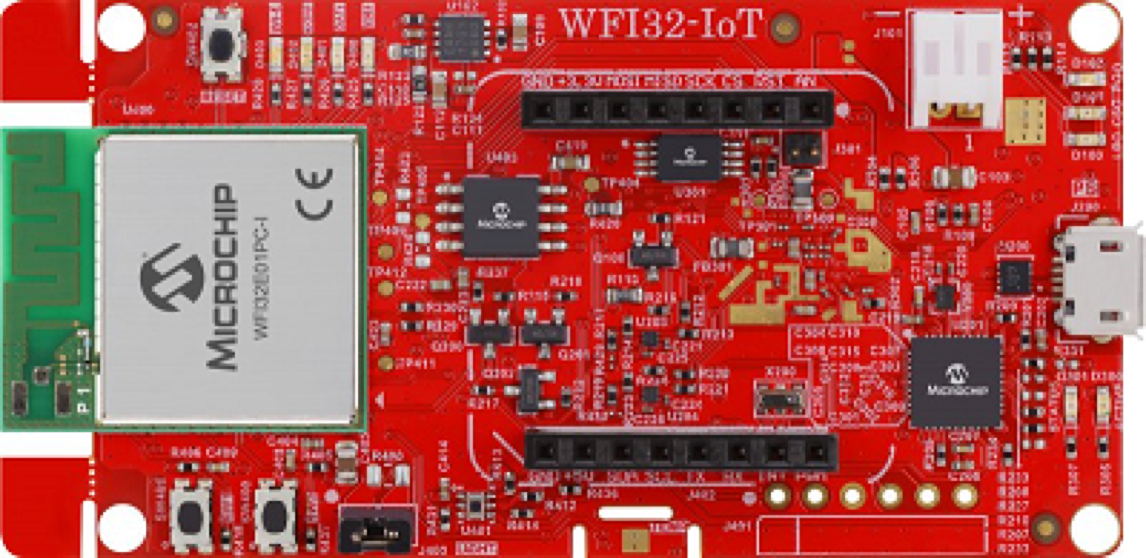


Single Board Computer (SBC)
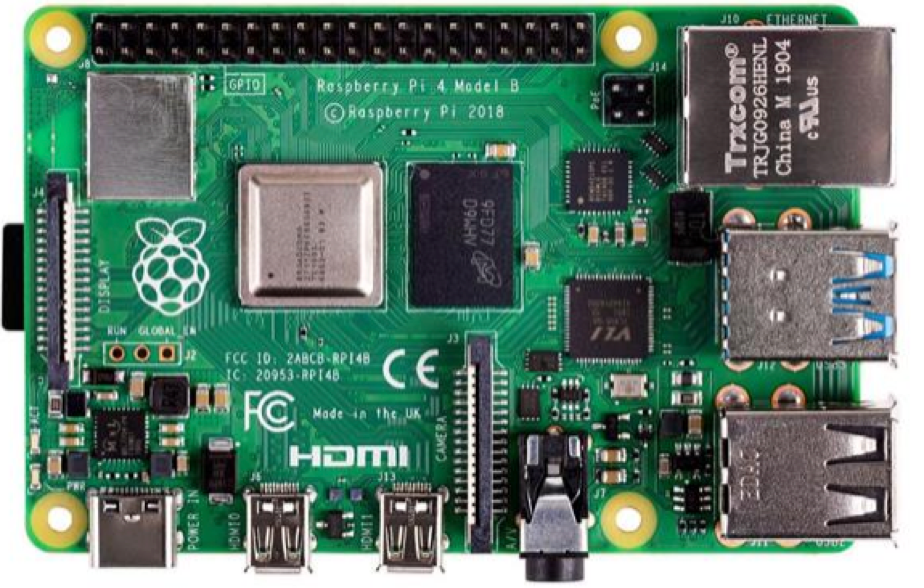

Wi-Fi Network Controller and Processors
A network processor is a device (integrated circuit) with network application features, such as adding Wi-Fi to MCUs to enable cloud connectivity. A Wi-Fi network processor can be external or built-in the microcontroller (MCU)